Resting-state network topology characterizing callous-unemotional traits in adolescence
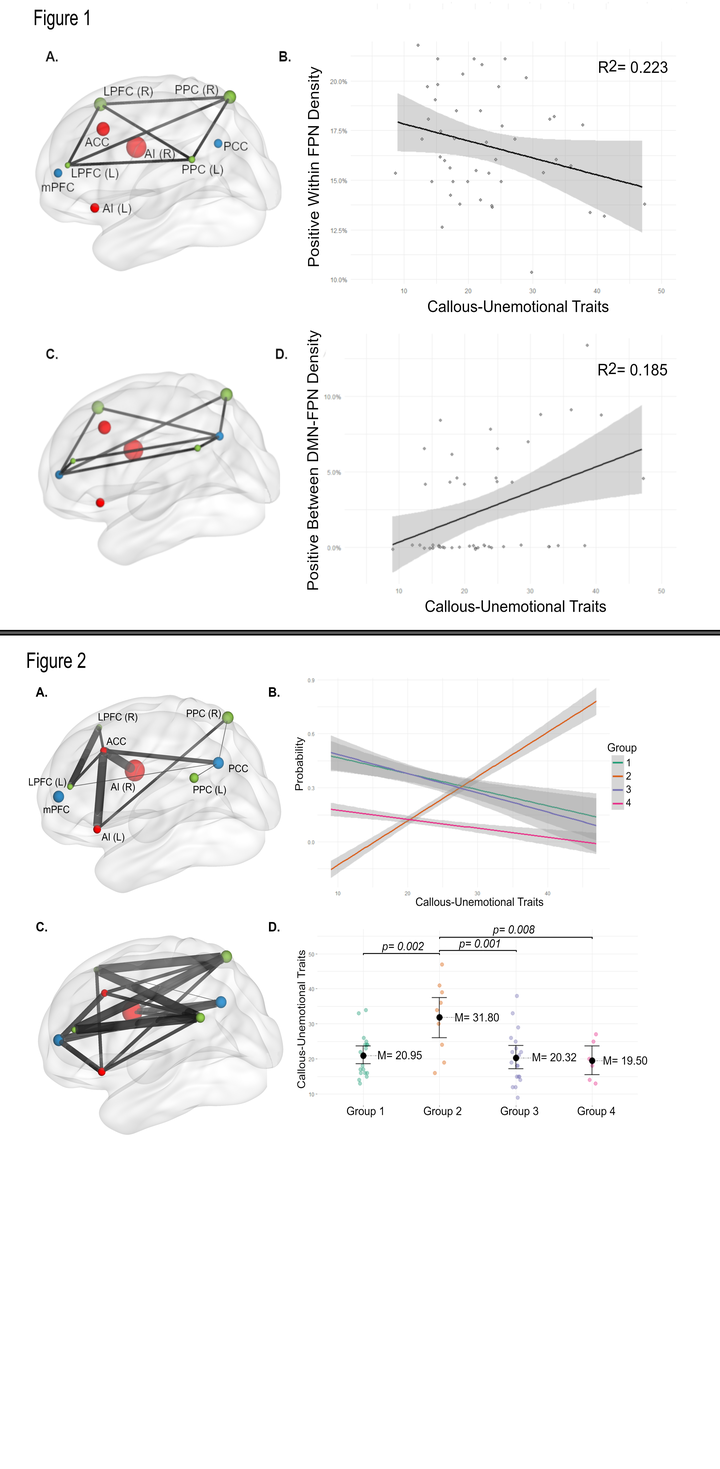 Figure 1. Individual-level associations across all participants with callous-unemotional traits. A. Depiction off all potential connections in the frontoparietal network (FPN); B. Association between positive connections within the FPN; C. Depiction of all possible connections between default mode-frontoparietal networks (DMN-FPN); D. Association between CU traits and positive connections between DMN-FPN. Node: blue = DMN, red = salience network (SAL), green = FPN.;Figure 2. Group-level associations of subgroup two with callous-unemotional traits. A. Depiction of the shared connections for subgroup two. Size of spherical nodes indicate within network centrality (bigger node spheres = more centrality) and size of edges indicate connection density (thicker connection = more density); B. Depicting probability of subgroup inclusion in the presence of total callous-unemotional traits; C. Depicting the heterogeneity of all unshared connections in subgroup 2; D. Mean differences in CU traits by GIMME identified network subgroup. Note: only significant pairwise tests are shown. Node colors: blue = default mode network, red = salience network, green = frontoparietal network.
Figure 1. Individual-level associations across all participants with callous-unemotional traits. A. Depiction off all potential connections in the frontoparietal network (FPN); B. Association between positive connections within the FPN; C. Depiction of all possible connections between default mode-frontoparietal networks (DMN-FPN); D. Association between CU traits and positive connections between DMN-FPN. Node: blue = DMN, red = salience network (SAL), green = FPN.;Figure 2. Group-level associations of subgroup two with callous-unemotional traits. A. Depiction of the shared connections for subgroup two. Size of spherical nodes indicate within network centrality (bigger node spheres = more centrality) and size of edges indicate connection density (thicker connection = more density); B. Depicting probability of subgroup inclusion in the presence of total callous-unemotional traits; C. Depicting the heterogeneity of all unshared connections in subgroup 2; D. Mean differences in CU traits by GIMME identified network subgroup. Note: only significant pairwise tests are shown. Node colors: blue = default mode network, red = salience network, green = frontoparietal network.
Abstract
Background Callous-unemotional (CU) traits, a youth antisocial phenotype, are hypothesized to associate with aberrant connectivity (dis-integration) across the salience (SAL), default mode (DMN), and frontoparietal (FPN) networks. However, CU traits have a heterogeneous presentation and previous research has not modeled individual heterogeneity in resting-state connectivity amongst adolescents with CU traits. The present study models individual-specific network maps and examines topological features of individual and subgroup maps in relation to CU traits. Methods Participants aged 13-17 completed resting-state functional connectivity and the inventory of callous-unemotional traits as part of the Nathan Klein Rockland study. A sparse network approach (GIMME) was used to derive individual-level and subgroup maps of all participants. We then examined heterogeneous network features associated with CU traits. Results Higher rates of CU traits increased probability of inclusion in one subgroup, which had the highest mean level of CU traits. Analysis of network features reveals less density within the FPN and greater density between DMN-FPN associated with CU traits. Discussion Findings indicate heterogeneous person-specific connections and some subgroup connections amongst adolescents associate with CU traits. Higher CU traits associate with lower density in the FPN, which has been associated with attention and inhibition, and higher density between the DMN-FPN, which have been linked with cognitive control, social working memory, and empathy. Our findings suggest less efficiency in FPN function which, when considered mechanistically, could result in difficulty suppressing DMN when task positive networks are engaged. This is an area for further exploration but could explain cognitive and socio-affective impairments in CU traits.
Citation:
Winters, D. E., Sakai, J. T., & Carter, R. M. (2021). Resting-state network topology characterizing callous-unemotional traits in adolescence. NeuroImage: Clinical, 32, 102878.
Supplementry Material PDF