Executive function and underlying brain network distinctions for callous-unemotional traits and conduct problems in adolescents
Abstract
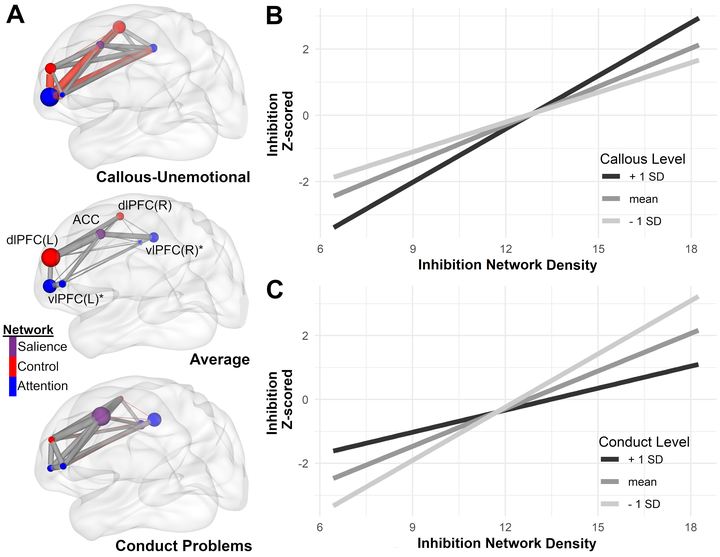
The complexity of executive function (EF) impairments in youth antisocial phenotypes of callous-unemotional (CU) traits and conduct problems (CP) challenge identifying phenotypic specific EF deficits. We can redress these challenges by (1) accounting for EF measurement error and (2) testing distinct functional brain properties accounting for differences in EF. Thus, we employed a latent modeling approach for EFs (inhibition, shifting, fluency, common EF) and extracted connection density from matching contemporary EF brain models with a sample of 112 adolescents (ages 13-17, 42% female). Path analysis indicated CU traits associated with lower inhibition. Inhibition network density positively associated with inhibition, but this association was strengthened by CU and attenuated by CP. Common EF associated with three-way interactions between density*CP by CU for the inhibition and shifting networks. This suggests those higher in CU require their brain to work harder for lower inhibition, whereas those higher in CP have difficulty engaging inhibitory brain responses. Additionally, those with CP interacting with CU show distinct brain patterns for a more general EF capacity. Importantly, modeling cross-network connection density in contemporary EF models to test EF involvement in core impairments in CU and CP may accelerate our understanding of EF in these phenotypes.
Citation:
Winters, D. E., Dugre, J., Sakai, J. T., & Carter, M. (2023). Executive function and underlying brain network distinctions for callous-unemotional traits and conduct problems in adolescents, bioRxiv 2023.10.31.565009; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.10.31.565009